| Документация | Нормативный документ | Форма | Образец |
| Реестр исполнительной документации | ВСН 012-88 (часть II) | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Специализированные журналы | |||
| Общий журнал работ | РД-11-05-2007 | скачать форму | скачать журнал |
| Журнал прокладки кабелей | И 1.13-07 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Журнал монтажа кабельных муфт напряжением выше 1000 В | И 1.13-07 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Журнал верификации закупленной продукции (журнал входного контроля) | ГОСТ 24297-2013 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Журнал авторского надзора за строительством (если по договору осуществляется авторский надзор) | СП 11-110-99 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Исполнительные схемы | |||
| Исполнительный чертеж сетей электроснабжения и электроосвещения | скачать форму | скачать образец | |
| Акты освидетельствования скрытых работ | скачать форму | скачать образец | |
| Монтаж кабеленесущих систем | РД-11-02-2006 | ||
| Монтаж кабельных линий и их крепление к конструкциям здания | РД-11-02-2006 | ||
| Монтаж заземляющих устройств | РД-11-02-2006 | ||
| Устройство прохода через стены и перегородки сетей электроснабжения и электроснабжения | РД-11-02-2006 | ||
| Акты, протоколы и прочие документы | |||
| Акт освидетельствования сетей инженерно-технического обеспечения | РД-11-02-2006 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Обложка к комплекту технической документации по сдаче-приемке электромонтажных работ | И 1.13-07 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
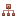
| Ведомость технической документации, предъявляемой при сдаче-приемке электромонтажных работ | И 1.13-07 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Акт технической готовности электромонтажных работ | И 1.13-07 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Ведомость изменений и отступлений от проекта | И 1.13-07 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Ведомость электромонтажных недоделок, не препятствующих комплексному опробованию | И 1.13-07 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
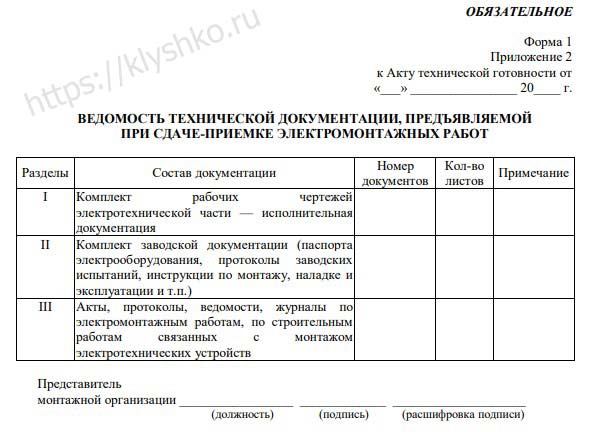
| Акт о приемке-передаче оборудования в монтаж | И 1.13-07 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Акт о выявленных дефектах оборудования | И 1.13-07 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Ведомость смонтированного электрооборудования | И 1.13-07 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Акт готовности строительной части помещений (сооружений) к производству электромонтажных работ | И 1.13-07 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Справка о ликвидации недоделок | И 1.13-07 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Акт передачи смонтированного оборудования для производства пусконаладочных работ | И 1.13-07 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Акт о приемке и монтаже силового трансформатора | И 1.13-07 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Протокол осмотра и проверки технической готовности электромонтажных работ по аккумуляторной батарее | И 1.13-07 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Ведомость замеров при контрольном разряде аккумуляторной батареи | И 1.13-07 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Акт осмотра канализации из труб перед закрытием | И 1.13-07 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Протокол испытаний давлением локальных разделительных уплотнений или стальных труб для проводок во взрывоопасных зонах классов В-1 и В-1а | И 1.13-07 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Акт приемки траншей, каналов, туннелей и блоков под монтаж кабелей | И 1.13-07 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Протокол осмотра и проверки сопротивления изоляции кабелей на барабане перед прокладкой | И 1.13-07 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Протокол прогрева кабелей на барабане перед прокладкой при низких температурах | И 1.13-07 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Акт осмотра кабельной канализации в траншеях и каналах перед закрытием | И 1.13-07 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Акт готовности монолитного бетонного фундамента под опору ВЛ | И 1.13-07 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Акт готовности сборных железобетонных фундаментов под установку опор ВЛ | И 1.13-07 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Паспорт воздушной линии электропередачи | И 1.13-07 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Акт замеров в натуре габаритов от проводов ВЛ до пересекаемого объекта | И 1.13-07 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Паспорт заземляющего устройства | И 1.13-07 | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Акт проверки осветительной сети на функционирование и правильность монтажа установочных аппаратов | Справочник ЦКС | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Акт проверки осветительной сети на правильность зажигания внутреннего освещения | Справочник ЦКС | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Акт проверки надежности крепления крюков под люстры и светильники | Справочник ЦКС | скачать форму | скачать образец |
| Акт рабочей комиссии о приемке оборудования после индивидуального испытания | скачать форму | скачать образец | |
| Протокол сопротивления изоляции проводов и кабелей | |||
| Протокол проверки полного сопротивления петли «фаза-нуль» | |||
| Протокол измерения сопротивления растеканию тока контура заземления (заземляющего устройства) | |||
| Протокол проверки целостности цепи заземления | |||
| Протокол определение удельного сопротивления грунта | |||
| Протокол проверки обеспечения условий срабатывания УЗО | |||
| Прочие документы | |||
| Копии удостоверений электротехнического персонала | |||
| Копия свидетельства об аттестации электролаборатории | |||
| Паспорта, сертификаты качества, пожарные сертификаты, санитарно-гигиенические заключения на строительные материалы, изделия и конструкции | |||
| Комплект рабочих чертежей на строительство предъявляемого к приемке объекта, разработанных проектными организациями, с надписями о соответствии выполненных в натуре работ этим чертежам или внесенным в них изменениям, сделанными лицами, ответственными за производство строительно-монтажных работ, согласованными с авторами проекта | |||
| Документы о согласовании отступлений от проекта при строительстве | |||
| Разрешительная документация | |||
| Информационный лист монтажной организации | |||
| Копия свидетельства СРО монтажной организации | |||
| Приказы на ответственные лица | |||
| Копии удостоверений персонала, занятого на электромонтажных работах | |||
| Рабочая документация со штампом Заказчика «В производство работ» | |||
| Проект производства работ (копия титульного листа и листа ознакомления) | |||
1. Реестр исполнительной документации
2. Общий журнал работ и специальные журналы работ:
3. Исполнительные схемы и чертежи:
- Исполнительный чертеж сетей электроснабжения и электроосвещения
4. Акты, протоколы приемки и испытаний, прочие документы:
- Акт готовности строительной части к производству электромонтажных работ
- Акт проверки осветительной сети на функционирование и правильность монтажа установленных автоматов
- Акт проверки надежности крепления крюков под люстры и светильники
- Акт проверки осветительной сети на правильность зажигания внутреннего освещения
- Ведомость технической документации, предъявляемой при сдаче-приемке электромонтажных работ
- Ведомость смонтированного электрооборудования
- Ведомость изменений и отступлений от проекта
- Протокол измерений сопротивления изоляции
- Протокол проверки полного сопротивления петля «фаза-ноль» (производится лабораторией)
- Протокол проверки обеспечения условий срабатывания УЗО (производится лабораторией)
- Акт технической готовности электромонтажных работ
5. Акт освидетельствования скрытых работ:
- Устройство прохода через стены и перегородки сетей электроснабжения и электроснабжения
- Монтаж заземляющих устройств
6. Инструкции по эксплуатации
7. Паспорта, сертификаты качества, пожарные сертификаты, санитарно-гигиенические заключения на строительные материалы, изделия и конструкции. На все поступающие на строительную площадку строительные материалы, изделия, конструкции и оборудование должен составляться акт входного контроля с последующим подписанием его ответственными лицами
8. Комплект рабочих чертежей на строительство предъявляемого к приемке объекта, разработанных проектными организациями, с надписями о соответствии выполненных в натуре работ этим чертежам или внесенным в них изменениям, сделанными лицами, ответственными за производство строительно-монтажных работ, согласованными с авторами проекта.
9. Документы о согласовании отступлений от проекта при строительстве
 Так же, как правило, в комплект приемо-сдаточной документации входит пакет разрешительной документации, со следующим составом:
Так же, как правило, в комплект приемо-сдаточной документации входит пакет разрешительной документации, со следующим составом:
1. Информационный лист монтажной организации
2. СРО монтажной организации
3. Приказы на ответственных представителей
4. Удостоверения на персонал (сварщики, электротехнический персонал и т.п.)
5. Рабочая документация со штампом Заказчика «В производство работ»
6. Проект производства работ (титульный лист и лист ознакомления)
Представленный состав исполнительной документации по разделу «Электрическое освещение» (ЭО) является приблизительным. Точный состав исполнительной документации зависит от требований заказчика.
Главная | Перечни исполнительной документации | Внутренние сети электроснабжения
- Журналы:
- Общий журнал работ;
- Журнал входного контроля качества.
- Исполнительные схемы:
- Исполнительный чертеж сетей электроснабжения и электроосвещения.
- Акты освидетельствования скрытых работ:
- Прокладка сетей электроснабжения и электроосвещения под штукатуркой;
- Устройство проходов через стены и перегородки сетей электроснабжения и электроосвещения.
- Акты испытаний и ведомости:
- Акт готовности строительной части к производству электромонтажных работ;
- Акт проверки осветительной сети на функционирование и правильность монтажа установленных автоматов;
- Акт проверки осветительной сети на правильность зажигания внутреннего освещения;
- Ведомость технической документации, предъявляемой при сдаче-приемке электромонтажных работ;
- Ведомость смонтированного электрооборудования;
- Ведомость изменений и отступлений от проекта;
- Протокол измерений сопротивления изоляции;
- Протокол проверки полного сопротивления петля «фаза-ноль»;
- Протокол проверки обеспечения условий срабатывания УЗО;
- Акт технической готовности электромонтажных работ;
- Акт допуска электроустановки в эксплуатацию.
- Сертификаты и паспорта качества на применяемые материалы и оборудование, санитарно-эпидемиологические заключения, сертификаты пожарной безопасности.
- Комплект рабочих чертежей на строительство предъявляемого к приемке объекта, разработанных проектными организациями, с надписями о соответствии выполненных в натуре работ этим чертежам или внесенным в них изменениям, сделанными лицами, ответственными за производство строительно-монтажных работ, согласованными с авторами проекта.
Примерный перечень исполнительной документации при монтаже систем электроснабжения и освещения
| 1 | Журналы | Общий журнал работ; |
|---|---|---|
| Журнал входного контроля качества; | ||
| 1 | Журналы | Общий журнал работ; |
| Журнал входного контроля качества; | ||
| 2 | Исполнительные схемы | Исполнительный чертеж сетей электроснабжения и электроосвещения. |
| 3 | Акты освидетельствования скрытых работ | Прокладка сетей электроснабжения и электроосвещения под штукатуркой; |
| Устройство проходов через стены и перегородки сетей электроснабжения и электроосвещения; | ||
| 4 | Акты испытаний и ведомости | Акт готовности строительной части к производству электромонтажных работ; |
| Акт проверки осветительной сети на функционирование и правильность монтажа установленных автоматов; | ||
| Акт проверки осветительной сети на правильность зажигания внутреннего освещения; | ||
| Ведомость технической документации, предъявляемой при сдаче-приемке электромонтажных работ; | ||
| Ведомость смонтированного электрооборудования; | ||
| Ведомость изменений и отступлений от проекта; | ||
| Протокол измерений сопротивления изоляции. | ||
| Протокол проверки полного сопротивления петля «фаза-ноль». | ||
| Протокол проверки обеспечения условий срабатывания УЗО. | ||
| Акт технической готовности электромонтажных работ. | ||
| Акт допуска электроустановки в эксплуатацию. | ||
| 5 | Сертификаты и паспорта качества на применяемые материалы и оборудование, санитарно-эпидемиологические заключения, сертификаты пожарной безопасности. | |
| 6 | Комплект рабочих чертежей на строительство предъявляемого к приемке объекта, разработанных проектными организациями, с надписями о соответствии выполненных в натуре работ этим чертежам или внесенным в них изменениям, сделанными лицами, ответственными за производство строительно-монтажных работ, согласованными с авторами проекта. | |


Здравствуйте, когда начинаешь разбираться в каком-нибудь новом деле то, кажется, что все очень сложно и трудно понять, как надо делать правильно. С исполнительной документацией по электрике, мне пришлось столкнуться в этом году на реконструкции промышленного объекта, работая инженером ПТО. В этой статье об составление исполниловки я расскажу не как электрик, а как птошник, который мало чего понимает в самих работах.

 Есть такой нормативный документ как «Инструкция по оформлению приемосдаточной документации по электромонтажным работам И 1.13-07» в котором расписан порядок оформления, показаны формы актов и порядок сдачи выполненных работ по электрики:
Есть такой нормативный документ как «Инструкция по оформлению приемосдаточной документации по электромонтажным работам И 1.13-07» в котором расписан порядок оформления, показаны формы актов и порядок сдачи выполненных работ по электрики:1. ОБЩИЕ ПОЛОЖЕНИЯ
1.1. Устанавливаются единые формы приемосдаточной документации по электромонтажным
работам.
1.2. Единые формы приемосдаточной документации охватывают все виды
электромонтажных работ, на которые распространяются требования СНиП 3.05.06-85
«Электротехнические устройства».
Инструкция не распространяется на оформление приемосдаточных документов:
— на ревизию, сушку, ремонт электрооборудования и пусконаладочные работы;
— на монтаж электрических машин;
— на монтаж контактных сетей промышленного и городского электрифицированного
транспорта.
1.3. Комплексная приемка оборудования в целом, включая электрооборудование,
осуществляется рабочей комиссией, назначенной заказчиком (застройщиком), при этом
составляется акт рабочей комиссии о приемке оборудования после индивидуального испытания
(форма 1а).
Актом оформляется передача заказчику оборудования всего объекта или по отдельным
установкам на крупных и сложных объектах. Актом также удостоверяется, что оборудование
отвечает требованиям приемки для его комплексного опробования.
В инструкции показаны примеры формы актов, ведомостей и журналов, остается только разобраться, как эти формы заполнять и к каким электромонтажным работам из проекта они относятся.
Исполнительная документация по электрике, пример
 Давайте на примере одного из проектов, который мы делали, разберемся, как правильно оформлять исполнительную документацию по электрике. Проект по разделу ЭМ (силовое электрооборудование), который состоит из таких чертежей как:
Давайте на примере одного из проектов, который мы делали, разберемся, как правильно оформлять исполнительную документацию по электрике. Проект по разделу ЭМ (силовое электрооборудование), который состоит из таких чертежей как:- Общие данные;
- Технологическая схема с перечнем электроприводов;
- Принципиальная схема распределительной системы;
- Схема электрическая принципиальная управления задвижками. Схема подключения клеммой коробки;
- Схема электрическая принципиальная управления насосом;
- Перечень электроприводов с условиями управления;
- Подключения кабелей к клемникам контролера;
- План расположения электрооборудования и прокладки электрических сетей;
- Схема заземления;
- Кабельнотрубный журнал.
В общестрое прораб должен ежедневно вести исполнительную документацию, принимать материалы, заполнять спецжурналы, составлять и подписывать различные акты. Электрика не исключение ответственное лицо за выполнение данного вида работ должен изучить проект, составить заявки на материалы или получить оборудование у заказчика, ежедневно заполнять спецжурналы, составлять и подписывать акты.
Сейчас во многих строительных фирмах составление исполнительной документации скидывают на инженеров ПТО и электрика не исключение, почему так происходит, читайте в этой статье.
Подрядчик, принимая оборудования в монтаж, от заказчика должен оформить и подписать акт по форме ОС-15 «Акт о приемке-передаче оборудования в монтаж». Если подрядчик находит дефекты в передаваемом оборудование, то заполняется форма ОС-16 «Акт о выявленных дефектах оборудования».
 А бывает и такое прораб или рабочий (прораб может отправить рабочего на склад заказчика) принимает оборудование от заказчика и не делает входной контроль, во время монтажа обнаруживают дефекты, тогда заказчику трудно будет что-то предъявить. Представители заказчика могут сказать, что вы приняли, в накладной расписались, при передачи никто не говорил, что есть дефекты, значит, вы испортили во время монтажа.
А бывает и такое прораб или рабочий (прораб может отправить рабочего на склад заказчика) принимает оборудование от заказчика и не делает входной контроль, во время монтажа обнаруживают дефекты, тогда заказчику трудно будет что-то предъявить. Представители заказчика могут сказать, что вы приняли, в накладной расписались, при передачи никто не говорил, что есть дефекты, значит, вы испортили во время монтажа.Такие моменты должен знать производитель работ или инженер МТО (материально-технического обеспечения), а если вы работаете в ПТО (производство-техническом отделе), то вам стоит напомнить прорабу, что он при получении оборудования он должен оформить форму ОС-15 и отдать ее вам.
Вся исполнительная документация по разделу ЭМ состоит из следующих актов:
- Ведомость технической документации;
- Акт технической готовности;
- Ведомость изменений и отступлений от проекта;
- Ведомость смонтированного оборудования;
- Протокол измерения сопротивления изоляции;
- Протокол на барабане перед прокладкой;
- Журнал прокладке кабелей;
- Ведомость передаваемых паспортов и сертификатов на оборудование;
- Акт готовности строительной части помещений к производству электромонтажных работ;
- Акт передачи смонтированного оборудования.
Примеры заполнения данных актов и протоколов можно посмотреть здесь Перед началом реализации проекта заказчик должен предоставить приказы на ответственные лица, которые будут проверять и принимать выполненные работы.


При оформлении исполнительной документации по электрики, к ведомости передаваемых паспортов и сертификатов на оборудование необходимо приложить все эти документы.
Обычно это большая проблема, так как во время монтажа рабочие, распаковывая оборудование, сертификаты и паспорта выкидывают, которые обычно вложены в коробки с оборудованием или прикреплены на барабаны с электрическими кабелями, так как считают, что эти бумаги никому не нужны. Некоторые прорабы не собирают эти документы и не предупреждают рабочих, чтоб ему их сдавали, может по не знанию, а может из-за разгильдяйства.
А инженеры ПТО, которые в конечном итоге комплектуют исполнительную документацию, не могут найти паспорта, сертификаты на материалы и электрические кабеля. В этом случае приходиться созваниваться с поставщиками и просить у них, чтоб еще раз предоставили все сопутствующие документы.
Нужна ли исполнительная схема в исполнительной документации по электрике читайте в статье «Исполнительная схема по электрике».
Есть вопросы по исполнительной документации по электрике напишите в комментариях постараюсь помочь.
С уважением, Олег Клышко
Ваша благодарность за мою статью это клик по любой кнопке ниже. Спасибо!
Исполнительная документация, оформленная соответствующим образом, является документом построенного здания или сооружения, облегчающим процесс эксплуатации, отражающим техническое состояние, дающим четкое представление об ответственных производителях работ по любому из видов выполненных работ.
Исполнительная документация делится на исполнительную производственную документацию (первичные документы о соответствии) и исполнительную документацию.
Исполнительная производственная документация (первичные документы о соответствии) — это документация, оформляемая в процессе строительства и фиксирующая процесс производства строительно-монтажных работ, а также технического состояния объекта. Состав первичных документов о соответствии определяется строительными нормами и правилами в установленном порядке и проектом (акты промежуточной приемки ответственных конструкций, акты освидетельствования скрытых работ, акты испытаний, документы лабораторного контроля, сертификаты, исполнительные геодезические съемки, журналы работ). Эти первичные документы комплектуются генеральным подрядчиком и контролируются техническим надзором заказчика. Документы передаются генподрядчиком заказчику по перечню, который является приложением к перечню основных документов. Исполнительная производственная документация необходима на время производства работ для обеспечения и подтверждения ведения строительного контроля.
Комплект первичной документации после ввода объекта в эксплуатацию передается заказчиком в установленном порядке эксплуатирующей организации для постоянного хранения. (МГСН «Приемка и ввод в эксплуатацию законченных строительством объектов. Основные положения»)
Исполнительная документация (исполнительные чертежи) — это комплект рабочих чертежей с надписями о соответствии выполненных в натуре работ этим чертежам или о внесенных в них по согласованию с проектировщиком изменениях, сделанных лицами, ответственными за производство строительно-монтажных работ (СНиП 3.01.04-87 «Приемка в эксплуатацию законченных строительством объектов. Основные положения»). Исполнительная документация подтверждает выполнение работ в соответствии с проектными решениями, техническими регламентами и необходима для обеспечения эксплуатации зданий, строений и сооружений.
В общем случае исполнительные чертежи выполняются в четырех экземплярах: один экземпляр передается заказчику, два — эксплуатационной организации. Один экземпляр остается в организации, проводившей работы.
Исполнительная документация подлежит хранению у застройщика или заказчика до проведения органом государственного строительного надзора итоговой проверки. На время проведения итоговой проверки исполнительная документация передается застройщиком или заказчиком в орган государственного строительного надзора. После выдачи органом государственного строительного надзора заключения о соответствии построенного, реконструированного, отремонтированного объекта капитального строительства требованиям технических регламентов (норм и правил), иных нормативных правовых актов и проектной документации исполнительная документация передается застройщику или заказчику на постоянное хранение.
РД-11-02-2006. — документ, определяющий состав и порядок ведения исполнительной документации при строительстве, реконструкции, капитальном ремонте объектов капитального строительства и требования, предъявляемые к актам освидетельствования работ, конструкций, участков сетей инженерно-технического обеспечения.
Подготовка исполнительной документации может осуществляться как в бумажном так и электронном виде, но приемка органами государственного строительного надзора ведется только в бумажном виде.
1. Сводный перечень исполнительной документации.
2. РД-11-02-2006. ТРЕБОВАНИЯ к составу и порядку ведения исполнительной документации при строительстве, реконструкции, капитальном ремонте объектов капитального строительства и требования, предъявляемые к актам освидетельствования работ, конструкций, участков сетей инженерно-технического обеспечения .
3. ОФОРМЛЕНИЕ ПЕРВИЧНЫХ ДОКУМЕНТОВ.
4. Перечень ИД при сдаче ТП.
5. Перечень ИД при сдаче ВЛ до 10кВ.
6. Перечень ИД при сдаче КЛ до 10 кВ.
7. Перечень ИД при сдаче РП, ЗТП, КТП.
8. Перечень ИД при сдаче ЗРУ 10кВ.
9. Перечень ИД при сдаче ПС 110-220.
10. Исполнительная документация в строительстве. Справочное пособие.
11. Комплект ИД для МКС-филиала МОЭСК
12. И 1.13-07. Инструкция по оформлению приемо-сдаточной документации по электромонтажным работам.
13. РД-11-05-2007. Порядок ведения общего и (или) специального журнала учета выполнения работ при строительстве, реконструкции, капитальном ремонте объектов капитального строительства.
14. Перечень актов по кабельным линиям для сдачи исполнительной и технической документации в МКС.
15. Перечень актов по ТП и РТП для сдачи в МКС исполнительной и технической документации.
Исполнительная схема электроснабжения — Energy
Исполнительная схема электроснабжения


Наиболее простым вариантом является однолинейная исполнительная схема электропроводки — она отличается от прочих тем, что в ней любые линии указываются в виде одной черты с условными обозначениями, описывающими их характеристики. Кроме того, схемы также могут быть принципиальными – они содержат в себе абсолютно все подробности формируемой электрической сети и используются для согласования ввода в эксплуатацию с государственными надзорными органами. Также существуют монтажные планы, которые необходимы для проведения связей электросетей с общими архитектурными, дизайнерскими чертежами и исполнительной схемы электропроводки.
Исполнительные схемы
Важнейшей классификацией является деление планов по периоду формирования. На стадии проектирования создается расчетная, а при непосредственном монтаже и запуске – исполнительная схема электроснабжения.
Пример проекта электроснабжения ресторана
Исполнительная отличается от расчетной тем, что в ней отображены все изменения в технических решениях, произведенные по той или иной причине в процессе установки. Главным пользователем исполнительной схемы является заказчик или собственник объекта, так как она необходима ему для организации ремонта, обслуживания и модификации без необходимости проведения дополнительных электротехнических исследований.


Исполнительная схема электроснабжения строится в соответствии с государственными и международными стандартами проектирования электрических систем. Для этого используется ряд условных обозначений, а также маркировок оборудования и силовых линий. Именно поэтому такую работу должен выполнять профессионал высокой квалификации – ошибка приведет к невозможности согласования запуска системы, а также к возникновению значительных проблем в будущем.
Связь с другими схемами
Любая исполнительная схема электроснабжения создается на основе принципиального чертежа, что обеспечивает ей соответствие изначально созданному проекту. Однако в ней допускается применение некоторой доли изменений, которые призваны усовершенствовать систему, сделав ее более эффективной или экономичной. Все пояснения к изменениям отражаются в специальных журналах, актах, протоколах и прочей исполнительной документации. При этом обязательно указывается причина, так как ее отсутствие является нарушением договора на осуществление работ.


В свою очередь, такое графическое отображение служит основой для монтажной схемы. В ней нет множества подробностей, однако четко указываются размеры оборудования, сечение кабелей, а также характеристики электрического тока на том или ином участке. За счет приведения плана работ в соответствие с архитектурной и дизайнерской концепцией данная схема способна упростить выполнение большинства процессов, а также уменьшить прайс на электромонтажные работы за счет исключения необходимости разрушения отделки и конструктивных элементов, изначально не предназначенных для монтажа электрооборудования.
Ниже вы можете воспользоваться онлайн-калькулятором для рассчёта стоимости проектирования сетей электроснабжения:
Поделитесь ссылкой
Дата публикации: 22.09.2014
90000 Circuit, Different Types and Their Working 90001 90002 The power supply is the essential component in every electrical or electronic system. There are various requirements that need to be considered while choosing an exact power supply such as; necessities of power for the circuit or load mainly include voltage and current. The safety features of the power supply circuit like current and voltage limits for protecting the load, efficiency, physical size, and system noise immunity. In this article, we look into the 90003 definition of a power supply 90004, 90003 different types of power supplies 90004 and how they work.These power supplies are mainly used for measurement, maintenance, test, and product expansion activities. 90007 90008 90003 What is a Power Supply? 90004 90011 90002 The power supply can be 90003 defined 90004 as it is an electrical device used to give electrical supply to electrical loads. The main function of this device is to change the electrical current from a source to the accurate voltage, frequency and current to supply the load. Sometimes, these power supplies can be named to as electric power converters.Some types of supplies are separate pieces of loads, whereas others are fabricated into the appliances that they control. 90007 90016 90003 Power Supply Circuit 90004 90019 90002 The Power supply circuit is used in various electrical & electronic devices. The power supply circuits are classified into different types based on the power they utilize for providing for circuits or devices. For instance, the microcontroller based circuits are generally the 5V DC regulated power supply (RPS) circuits, which can be designed with the help of different method for changing the power from 230V AC to 5V DC.90007 90002 The power supply circuit is shown above, and the step by step conversion of 230V AC to 12V DC is discussed below. 90007 90024 90025 A step-down transformer converts the 230V AC into12v. 90026 90025 The bridge rectifier is used to change AC to DC 90026 90025 A capacitor is used to filter the AC ripples and gives to the voltage regulator. 90026 90025 Finally voltage regulator regulates the voltage to 5V and finally, a blocking diode is used for taking the pulsating waveform. 90026 90033 90034 90034 90002 Power Supply Block Diagram 90007 90038 90008 90003 Different Types of Power Supplies 90004 90011 90002 The different types of power supplies are classified as follows.90007 90016 90003 1) SMPS- Switched Mode Power Supply 90004 90019 90002 An SMPS power supply or computer power supply is one type of power supply that includes a switching regulator for converting electrical-power powerfully. Similar to other power supplies, this power supply transmits the power from a DC source or AC source to DC loads, such as a PC (personal computer), while changing the characteristics of current and voltage. Please refer this link to know more about Know All about Switch Mode Power Supply 90007 90051 90051 90002 SMPS — Switched Mode Power Supply 90007 90016 90003 2) Uninterruptible Power Supply 90004 90019 90002 A UPS (uninterruptible power supply) is an electrical device that permits a PC to keep working for some time as the main power supply is lost.This device is also given protection from power flow. 90007 90061 90061 90002 UPS — Uninterruptible Power Supply 90007 90002 A UPS includes a battery to store the energy when the device detects a power loss from the main source. For instance, if you are using the PC when the uninterruptible power supply senses the power loss, then you have to save the data before the UPS (secondary power source) discharges. 90007 90002 When both the primary and secondary power sources run out, any data in your PC’s RAM (random access memory) is erased.When power loss occurs, a secondary power source stops the loss of power so that it does not harm the personal computer. Please refer this link to know more about Uninterruptible Power Supply Circuit Diagram and Working 90007 90016 90003 3) AC Power Supply 90004 90019 90002 Typically, an AC power supply acquires the voltage from the mains supply and the voltage can be step up or step down by using a transformer to the required voltage and some filtering may take place. The different types of AC power supplies are designed to offer an almost stable current, and o / p voltage may change based on the load’s impedance.In some cases, as the power supply is DC, a step-up transformer and an inverter may be utilized for converting it into AC power. Some sorts of AC power alteration do not use a transformer. 90007 90075 90075 90002 AC Power Supply 90007 90002 If the input and output voltages are the similar and main function of the apparatus is to filter AC power. If the apparatus is designed for providing backup power, then it may be named as an uninterruptable power supply (UPS). At present, AC power supplies are classified into two types namely single phase systems as well as three phase systems.The main differences between these two are dependability of delivery. These supplies can also be applicable for changing the voltage as well as frequency. 90007 90016 90003 4) DC Power Supply 90004 90019 90002 A DC power supply is one that provides a consistent DC voltage to its load. Based on its plan, a DC power supply might be controlled from a DC supply or from an AC supply like the power mains. 90007 90087 90087 90002 DC Power Supply 90007 90016 90003 5) Regulated Power Supply 90004 90019 90002 An RPS (regulated power supply) is a fixed circuit used to change unregulated alternating current into a stable direct current.90007 90002 Here rectifier is used to change AC supply to DC, and its main function is to give a stable voltage to a device or circuit that should be functioned in a particular limit of the power supply. The output of the RPS may be changing (or) unidirectional, but it always DC (direct current). 90007 90099 90099 90002 Regulated Power Supply 90007 90002 The sort of stabilization used can be controlled to ensuring that the o / p remains in certain restrictions beneath various load conditions.90007 90016 90003 6) Programmable Power Supply 90004 90019 90002 This type of power supply permits remote control for its operation via analog input otherwise digital interfaces like GPIB or RS232. The controlled properties of this supply include current, voltage, frequency. These type of supplies are used in a wide range of applications like fabrication of semiconductors, X-ray generators, monitoring of crystal growth, automated apparatus testing. 90007 90002 Generally, these types of power supplies use an essential microcomputer for controlling as well as monitoring the operation of a power supply.A power supply provided with an interface of computer uses standard (or) proprietary communication protocols, and device control language like SCPI (standard-commands-for-programmable-instruments) 90007 90016 90003 7) Computer Power Supply 90004 90019 90002 The power supply unit in a computer is the part of the hardware that is used for changing the power supplied from the outlet into utilizable power for the several parts of the computer. It converts the alternating current into direct current 90007 90002 It also controls over-heating through controlling voltage, which may modify manually or automatically based on the power supply.The PSU or power supply unit is also called as a power converter or a power pack. 90007 90002 In a computer, the internal components like cases, motherboards, & power supplies all available in different configurations, sizes which are known as form factor. All these three components must be well-matched to work appropriately together. 90007 90016 90003 8) Linear Power Supply 90004 90019 90002 The LPS (linear power supply) or LR (linear regulator) circuit is used in various electrical & electronic circuits for supplying the DC current to the entire circuit.The linear power supply mainly includes a step-down transformer, rectifier, filter circuit & voltage regulator. The main function of this circuit is at first; step downs the alternating current voltage then changes it into direct current. The main features of this power supply include the following. 90007 90024 90025 The efficiency of this power supply ranges from 20 to 25% 90026 90025 The magnetic materials used in this power supply are CRGO core or St Alloy. 90026 90025 It is more reliable, less complex and bulky.90026 90025 It gives a faster response. 90026 90033 90002 The main advantages of linear power supply include reliability, simplicity, low cost and the noise level is low. Along with these benefits, there are some disadvantages such as 90007 90002 These are best for several low power applications as a result when a high-power is required; the drawbacks turn into more clearly. The disadvantages of this power supply include a high loss of heat, size, & low-efficiency level. Whenever linear power supply is used in high power applications; it requires large components to manage the power.90007 90002 Thus, this is all about different types of power supplies, and these are being used for providing the power supply to different systems efficiently. Power supplies are the essential components of every system to get electrical energy for the operation. So, some of the considerations of a power supply like design or development are more significant. Because day-by-day the invention of technology as well as power supplies are being increased for providing protection to electrical and electronic devices.90007.90000 Power supply of lighting circuits 90001 90002 The quality of the lighting 90003 90004 A source of comfort and productivity, lighting represents 15% of the quantity of electricity consumed in industry and 40% in buildings. The quality of the lighting (light stability and continuity of service) depends on the quality of the electrical energy thus consumed. The supply of electrical power to lighting networks has therefore assumed great importance. 90005 90004 To help with their design and simplify the selection of appropriate protection devices, the authors present in this document an analysis of the different lamp technologies and the main technological developments in progress.After summarizing the distinguishing features of lighting circuits and their impact on control and protection devices, they discuss the options concerning which equipment to use. 90005 90002 Artificial light 90003 90004 Artificial luminous radiation can be produced from electrical energy according to two principles: incandescence and electroluminescence. 90005 90012 Incandescence 90013 90004 This is the production of light via temperature elevation. The energy levels are plentiful, and in consequence, the emitted radiation spectrum is continuous.The most common example is a filament heated to white state by the circulation of an electrical current. The energy supplied is transformed into the Joule effect and into luminous flux. 90005 90012 Luminescence 90013 90004 This is the phenomenon of emission by a material of visible or almost visible luminous radiation. 90005 90020 90021 90022 Electroluminescence of gases 90023 90024 A gas (or vapors) subjected to an electrical discharge emits luminous radiation. Since this gas does not conduct at ordinary temperature and pressure, the discharge is produced by generating charged particles which permit ionization of the gas.The spectrum, in the form of stripes, depends on the energy levels specific to the gas or vapor used. The pressure and temperature of the gas determine the length of the emitted rays and the nature of the spectrum. 90025 90021 90022 Photoluminescence 90024 90023 This is the luminescence of a material exposed to visible or almost visible radiation (ultraviolet, infrared). 90025 90031 90004 When the substance absorbs ultraviolet radiationand emits visible radiation which stops a short time after energization, this is fluorescence.Not all the photons received are transformed into emitted photons. The best efficiency rating for existing fluorescent materials is 0.9. When the light emission persists after energization has stopped, it is phosphorescence. 90005 90004 90022 AUTHOR: 90024 Schneider Electric experts | Jacques SCHONEK, Marc VERNAY 90005 90004 90039 90005 .90000 Power Supplies Manufacturers Suppliers | IQS Directory 90001 90002 90003 business 90004 Industry Information 90005 90006 View A Video on Power Supplies — A Quick Introduction 90007 90002 Power Supplies 90005 90010 Power supplies, or power supply units (PSU), are devices that produce electrical power and provide reliable electrical currents that power electronics, machinery and devices for both industrial and commercial use. 90011 90012 90013 90014 90015 90016 90017 90015 90019 90017 90015 90022 90017 90024 90014 90015 90010 Power Supplies — Triad Magnetics 90011 90017 90015 90010 Power Supplies — Triad Magnetics 90011 90017 90015 90010 Power Supplies — Clark Power Systems Inc.90011 90017 90024 90014 90015 90041 90017 90015 90044 90017 90015 90047 90017 90024 90014 90015 90010 Power Supplies — Clark Power Systems Inc. 90011 90017 90015 90010 Power Supplies — Clark Power Systems Inc. 90011 90017 90015 90010 Power Supplies — Triad Magnetics 90011 90017 90024 90064 90065 90066 Applications 90067 90010 Power supplies can be integrated into a device or externally attached, portable modules, depending on their operating temperature and risk of overheating.PSUs are necessary to the operation of just about every electrical device, including: desktop computers (pc power control), laptop computers, cell phones, 90006 lasers 90007, ac 90006 power cords 90007, supply cords, telecommunications like radio, phone lines and the internet, medical equipment, lamps, appliances and industrial machinery. 90011 90010 They provide either 90006 AC power supply, 90007 which is an alternating current, or 90006 DC power supplies 90007, which offer a direct current.Today, most electronic devices in the home and office are powered by 12v power supply, while industrial applications employ high voltage power supply (high volt power supplies). 90011 90066 History 90067 90010 The power supply industry is relatively young; it began in the 1920s. The first power supply units were used to power commercial radios, as well as radios used in the home. In 1929 року, engineers figured out how to make radios with integrated power supply units. Between the 1930s and 1940s, manufacturers regulated power with vacuum tube linear regulators.They controlled the stable power channeled through these using knobs. While these worked, they were somewhat dangerous, as they became incredibly hot. Made from glass, the tubes could even turn red or melt. 90011 90010 In the ’50s, engineers came up with superconductors, including the transistor, which was originally perfected in 1947 at Bell Labs. Early transistors were smaller and much more efficient and reliable than vacuum tubes, which they quickly replaced. They were also safer than vacuum tubes.Unfortunately, they also presented new problems, namely their ability to only work with low to medium voltage systems. This changed in the early 1960s, when manufacturers began producing magnetic amplifiers (mag-amps). These worked by amplifying small signals and making them much stronger. These were quite durable and were used into the 1980s and 1990s. 90011 90010 In the 1960s, Dr. Kenneth Kupferberg patented the first designs for remotely controlled power supply systems. During this decade, when the world was slowing switching from analog to digital, scientists and engineers came up with all kinds of power supplying methods, including: linear series pass power supplies, high power operational amplifiers, bipolar source and sink units, ferroresonance, and control of input voltage and feedback control elements.90011 90010 In the 1970s, researchers paired high speed silicon transistors with low loss ferrite, a transformer core material. As as result, they were able to develop products that could work at high, inaudible frequencies upwards of 20KHz. In 1972, Hewlett Packard came out with a pocket calculator that they fueled with a switching power supply. Later in the ’70s, engineers figured out how to get linear power supplies to act based on the commands of a computer. This lead to the further development of digital controls.First of the digital controls was BCD (Binary Coded Decimal) digital control. Next was digital to analog power conversion (DAC), then the instrumentation bus standard. Hewlett Packard originally marketed it to the power supply industry as HPIB. Later, it was renamed RS232. This interface allowed for much faster and broader communications between power supplies and their controllers. 90011 90010 During the 1980s, as computers were being developed and digital products became more prominent, power supplies became that much more important.In response to demand, many new power supply companies cropped up all over the world. They helped power supplies to get even more powerful and easy to control. 90011 90010 The early ’90s saw power supplies manufacturers come out with smaller and smaller products. Because they were finding and creating stronger components, power supplies in the ’90s were more dense and far more efficient than anything made before. Today, power supplies are an integral part of our lives. In our digital world, we could not do without them.90011 90066 How It Works 90067 90010 PSUs work like this: 90011 90098 90099 They receive power, aka the input power, from a source such as a battery or wall socket. 90100 90099 They invert, convert or adapt the power. 90100 90099 They provide the converted power as an output power to an electronic device. 90100 90105 90010 There are two main types of electrical current that are regulated, controlled and altered by power supplies-alternating current and direct current.Both are used to power different kinds of electrical products, but the input into a power supply from a battery or other power source is almost always AC. 90011 90010 Alternating current exhibits electrical charge that consistently and periodically reverses direction. It moves forward then backwards over and over. This form of current is used in commercial businesses and residential buildings. The alteration of the current’s direction is measured in Hertz. For example, 60 Hertz refers to the number of alternative directions the current takes in a second.90011 90010 Direct current, on the other hand, refers to electric charge flow that runs in a single, linear direction. It flows in metal conductors like wires, semiconductors, insulators or even a vacuum. Cell phones and laptop computers use DC, as well as medical equipment, video technology and process control systems. Direct current units are usually external from the electronic device and held within a protective casing. 90011 90066 Types 90067 90010 There are many ways to group power supplies.First, there are variable power supplies and uninterruptible power supplies. 90011 90010 90006 Variable power supplies 90007 are able to adjust the output voltage to specific requirements for product testing and design. They are not super popular, though, because most electronic products today require regulated power supply. 90011 90010 90006 Uninterrupted power supplies (UPS) 90007 are backup power supply units that continue to provide power during the loss of AC input power. In other words, they provide stable and constant output at a certain, unwavering voltage regardless of power outages, brownouts or surges.These batteries work with the assistance of a DC / AC inverter or DC / DC converter. They can work as external units or internal units. External power units are called stand alone UPS units, while UPS units implanted in the equipment are called battery backup UPS units. 90011 90010 There are three types of uninterruptible power supplies (UPS): offline UPS, line interactive UPS and online UPS. 90011 90098 90099 90006 Offline UPS units 90007 are basically standby systems that provide battery power to equipment when the main power supplies fall below a set limit.These power supplies do not cost much and are recommended for home office use. 90100 90099 90006 Line interactive UPS units 90007 are similar to offline UPS units, in that they switch to battery mode during a blackout. However, these UPS units actually boost the main power supply when they fall, using a regulator. These power supplies are ideal for business applications. 90100 90099 90006 Online UPS units 90007 provide the highest level of protection for an electrical device. They supply critical power loads by converting AC to DC and then back to AC.These UPS units, often referred to as double conversions, contain an automatic bypass to ensure continuous power supplies during a short-term overload or UPS failure. Online UPS systems are perfect for critical loads and sensitive equipment, such as medical technology. 90100 90105 90010 90006 AC to DC converters 90007 convert power from an AC input, such as a wall outlet, into DC current. AC-DC power supplies are units that provide power to an electronic device by converting AC current, such as that which comes from a wall outlet, to DC current at the proper voltage.90011 90010 90006 Constant current power supplies 90007 control the output current for alterations in load, line and ambient temperature and time within particular limits. 90011 90010 90006 Constant voltage power supplies 90007 control the output voltage in load, line, ambient temperature and drift resulting from changes over time. 90011 90010 90006 DC / DC converters 90007 are used to increase or decrease the voltage level of DC electrical power, because, unlike AC, DC can not be changed using a 90006 transformer 90007.90011 90010 90006 DC power supplies 90007, such as linear power supplies, switching power supplies, DC / DC power converters and high voltage power supplies, receive an input power and output the required form of DC power. 90011 90010 90006 Ferroresonant power supplies 90007 are utilized at higher levels in static applications, due to their weight. Ferroresonant power supplies are effective only when the line frequency is extremely stable, as they are sensitive to changes of input AC frequencies.90011 90010 90006 Frequency converters, 90007 a special type of transducer, are simply electrical currents that convert periodic signals into their digital or analog equivalents. The most common frequency converters are frequency-to-digital and frequency-to-DC converters. 90011 90010 90006 Half bridge converters 90007 are power switching circuits consisting of two transistors and two capacitors. Half bridge converters function in similar fashion to full bridge converters. 90011 90010 90006 High voltage power supplies 90007 are capable of providing hundreds or thousands of volts from one or more DC outputs, using linear technology.Some high voltage power supplies have adjustable local or computer interface outputs and are used in specialized applications, including telecommunications, video technology and medical equipment. 90011 90010 90006 Power inverters 90007 change DC current to AC current and may be mechanical (e.g. motor), ferroresonant and solid state. 90011 90010 90006 Linear power supplies 90007 have a bulky steel or iron laminate transformer that acts as a safety barrier for the low voltage output from the AC input and reduces that input to a much lower voltage.The AC output is then rectified by two or four diodes, and electrical converters change the output into low voltage DC, which is regulated into the required output voltage by dropping the difference in voltage across the shunt regulator. 90011 90010 90006 Modular power supplies 90007 are comprised of a number of separate subsections, such as power, input and filter modules. 90011 90010 90006 Off-line power supplies 90007 operate directly off the AC line. Off-line power supplies do not use a power transformer before the process of rectification and filtering.90011 90010 90006 Operational powers supplies 90007 have a high open loop gain regulator, for which passive components can be used to program. The regulator acts like an operational amplifier. 90011 90010 90006 Rectifiers 90007 are electrical components containing sets of diodes that change AC into DC. They alter and regulate electrical current. 90011 90010 90006 Switch mode power supplies 90007 rectify and smooth AC voltage using diodes and capacitors, resulting in a high voltage DC, which in turn is converted by a small ferrite transformer and FETs or transistors into a safe, low voltage, high frequency voltage.Another set of diodes, capacitors and inductors convert that DC voltage into the required voltage, the corrections of which are done by adjusting the pulse width of the high frequency waveform. 90011 90066 Equipment Components 90067 90010 The equipment components of any given power supply unit depends entirely on its configuration and its application. In general, power supplies contain a power inverter, power converter or power adapter. 90011 90010 From there, they may have any number of components.Examples of various common power supply features include: adjustable voltage (which can be increased or decreased by a dial or knob), adjustable frequency, computer interface, 90006 fan 90007 cooling systems, as well as integral 90006 heatsink 90007 and overcurrent protection. 90011 90010 A good example of a piece of power supply equipment with some of these features is the power supply unit that provides electrical power for computers. This vital component is a smaller, black metal box typically located on the back of the computer in a corner of the case.It contains a power-cord receptacle and a cooling fan that is usually visible from the back of the system in which it is installed. 90011 90010 Many power supply units also work in conjunction with a backup battery that is employed in case of a power outage. Other features include: overvoltage protection, power factor correction, pure sine output, remote on and off switch, short circuit protection and water cooling. 90011 90066 Design and Customization 90067 90010 Power supply manufacturers offer many different designs and configurations of power supply units, which range depending on their application, type of current, frequency, power supply wattage and voltage level.When designing a custom power supply unit for you, or helping you pick a standard one, they consider specifications such as: the number of outputs, DC output voltage, DC output power, AC output voltage, AC output frequency, operating temperature and apparent power . 90011 90010 They make some unit designs and styles that are external, meaning they are separate components to the electronic device. These include board, cabinet, desktop, module, open frame, enclosed, rack mount and wall mount.They also make interior unit designs and styles. Generally, if their operating temperature is low enough, manufacturers will place many power supply units inside of the device. Manufacturers offer a variety of display choices in order to best provide you with provide information about the voltage and current that are the result of measuring and monitoring. Typical options include: digital numerical displays, analog visual indicators and graphic or video displays. 90011 90010 Learn about what custom options a specific supplier offers by checking out their website or talking to them directly.90011 90066 Safety and Compliance Standards 90067 90010 Power supplies are beholden to a wide range of safety and compliance standards. These vary based on your industry, application and location. Some of the major standards agencies around the world include: IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission), ISO (International Standards Organization), CSA (Canadian Standards Association) and UL (Underwriters Laboratories). Some offer guidance or requirements based on energy efficiency, while others discuss things like: insulation, voltage types, safety for medical use, safety in the lab, proper handling, etc.Find out what standard requirement certifications your power supplies should have by talking to your industry leaders. 90011 90066 Finding the Right Manufacturer 90067 90010 For the most efficient, highest quality and best-matched power supplies, you need to work with an experienced power supply provider. To find such a provider, check out the list we’ve provided on this page. All of those power supplies providers with whom we work have proven their worth to their customers time and time again.To find the right one for you, start by writing out a list of your specifications. Do not forget to include your budget, required lead times, delivery preferences, installation support preferences and post-installation support preferences. 90011 90236 90002 Power Supply Terms 90005 90010 — A sensing circuit for the input voltage located within the power supply that automatically switches to the necessary voltage range. 90240 90240 — The highest AC or DC voltage that may be applied from the input, output and / or chassis of a power supply.90240 90240 — Operating a newly manufactured power supply, usually at rated load, for a period of time in order to force early failures or other latent defects of the component before the unit is delivered to a customer. 90240 90240 — Noise that is typical of DC output and return lines with respect to input ground. 90240 90240 — The voltage output from a constant current power supply.90240 90240 — The removal of heat in a power supply by convection, forced air, radiation or liquid. Heat comes from regulation, transformation, filtering and rectification. 90240 90240 — The percent of voltage change at one output of a multiple output power supply resulting from the load change on another output. 90240 90240 — An overload protection circuit, which controls the highest output current of a power supply to safeguard the power supply or the load.90240 90240 — The projected lifetime of a power supply during which it will run at its stated specifications. 90240 90240 — Also referred to as «ripples,» it is the noise measured between the DC output and the output return. 90240 90240 — With operating parameters including line, load and ambient temperature held constant, it is the change in output voltage, following a warm-up period, over a certain period of time.90240 90240 — The ratio of power in terms of the input power against the output power. Efficiency is measured at full load and nominal line conditions. 90240 90240 — Also known as «radio-frequency interference (RFI), «it is unwanted high frequency energy conducted through the input or output lines of switching power supplies or radiated through space.EMI is caused by the switching transistors, output rectifiers and zener diodes. 90240 90240 — A current limiting circuit that, when under overload conditions, will gradually decrease the output current to a specified minimum current level under a direct short circuit. 90240 90240 — An electrical connection to earth that has a zero voltage or another conductor connected to earth.90240 90240 — The capability of remotely switching off the output power of a power supply. 90240 90240 — A low-pass or band-reject filter used to decrease the noise fed to the supply. Input line filters are located at the input of a power supply and may be external. 90240 90240 — The highest AC or DC voltage that can be continuously run from a power supply chassis or from input to output.90240 90240 — Altering a power supply output voltage, either higher or lower from its minimal setting, in order to confirm the system performance margin in respect to the supply voltage. Margining is typically done electrically via a system generated control signal. 90240 90240 — The least amount of load current or power that needs to be drawn from the power supply in order for the supply to meet its performance specifications.90240 90240 — A feature of a converter such that it continues to provide voltage to a load at a set upper limit without turning off and without necessitating a reset when the overvoltage event ceases. 90240 90240 — A circuit that either shuts down the power supply or shorts the power supply to ground if an overvoltage condition occurs.90240 90240 — The connection of the outputs of multiple power supplies with the same output voltage that are designed to share a load. The parallel operation generates a higher output current than would be available from a single supply. 90240 90240 — The absolute highest output power that a power supply can create without immediate damage. Typically, peak power is much higher than the continuous reliable output capacity and ought to be utilized rarely.90240 90240 — A signal from the power supply interface that relays a warning that the input voltage is not sustaining full power regulated output. 90240 90240 — A protection circuit that prevents damage to the power supply if a reverse voltage is applied at either the output or input terminals. 90240 90240 — A conductive path to earth intended to safeguard people from electrical shock by shunting away any dangerous currents that could happen from accident or malfunction.90240 90240 — Also known as «warm up time,» it is the time a converter needs to start running within specification after proper power has been applied. 90011 90295 90240 90240 90006 90006 90006 90301 90302 90295 90240 90007 90007 90007 .90000 EEP — Electrical Engineering Portal 90001 90002 90002 90004 90004 90006 My experience and guidance in the design and electrification of a modern airport 90007 90008 The electrical systems for airports require proper quality installations and consideration for features usually not involved in other electrical installations.In this article, we will be discussing the general elements … … 90009 90010 PREMIUM Membership Required 90011 This content is available for 90012 Premium members only 90013. Get access to premium HV / MV / LV technical articles, electrical engineering guides and research studies. 90014 Apply a 20% discount code 90012 99AF8 90013 for a 1-year plan! Login ♛Sign Up ♛ 90008 Jun 29, 2020 | Low Voltage ♛ 90009 90019 90019 90021 90021 90023 90023 90025 90025 90006 A real-life case study of relay coordination (step by step tutorial with analysis) 90007 90008 I would say that coordination is a TEAMWORK.In the protection context, it implies how the various protection devices in an electrical distribution network, work as a team, to achieve … … 90009 90010 PREMIUM Membership Required 90011 This content is available for 90012 Premium members only 90013. Get access to premium HV / MV / LV technical articles, electrical engineering guides and research studies. 90014 Apply a 20% discount code 90012 99AF8 90013 for a 1-year plan! Login ♛Sign Up ♛ 90008 Jun 15, 2020 | Energy and Power ♛ 90009 90040 90040 90042 90042 90044 90044 90006 My worst experience in the maintenance and supervision of medium voltage substations 90007 90008 While there are various voltage levels applicable across the globe depending upon the usability, the category of Medium Voltage remains one of the most critical voltage group comprising primary distribution …… 90009 90010 PREMIUM Membership Required 90011 This content is available for 90012 Premium members only 90013. Get access to premium HV / MV / LV technical articles, electrical engineering guides and research studies. 90014 Apply a 20% discount code 90012 99AF8 90013 for a 1-year plan! Login ♛Sign Up ♛ 90008 Jun 01, 2020 | Maintenance ♛ 90009 90059 90059 .